- Tech, OC'ing, SEO and more
- Hits: 123935
Article Index
BIOS Settings.
What is VDDCR CPU Load Line Calibration?
CPU LLC adds extra voltage to compensate for Vdroop when a CPU or GPU is put under heavy load. LLC gives overclocking stability by preventing low or high voltage fluctuations and tries to maintain a stable voltage supply to the CPU or GPU. Higher LLC tends to overshoot more in voltage supply, and a lower LLC tends to undershoot in the voltage supply to the CPU.
What is VDDCR CPU Current Capability?
It is a threshold for the VRM to shut down and monitors the current supply to the CPU, setting Current Capability higher will allow for more current supply to the CPU but will increase heat output. This works best if you have an overclock that shuts down the motherboard/PC because the threshold is triggered.
What is VDDCR CPU Switching Frequency?
Switching frequency is the transient response of your VRM MOSFETs settings this higher in Mhz will allow for a better transient response at the expense of increased heat output and using a lower setting in Mhz will lower the heat output but lower the transient response. Better transient response in overclocking translates into a more stable voltage supply from your PSU to the CPU.
What is VDDCR CPU Power Duty Control?
This will allow for setting the current supply to the internal CPU voltage regulator at the expense of increased heat when set to extreme and lower heat when using optimized or standard. This will help with stability in overclocking and give the best result when using optimized or extreme.
What is VDDCR CPU Power Phase Control?
This affects your VRM Power Phases to the CPU and will be depending on the setting, achieve greater stability in overclocking. Setting Power Phase Control to extreme keeps the number of active CPU power phases at the maximum. If you set Power Phase Control to optimized, there will be a power-saving, but less stability, phases to the CPU will power down.
What is SOC?
SOC(AMD) stands for System On Chip and is also known as uncore(Intel) and encompasses all the components, not in the core of the actual CPU but on the same substrate like internal GPU, Cache, I/O Ports, Memory Controller etc. Overclocking SOC settings can help in varying degrees with keeping CPU core components stable.
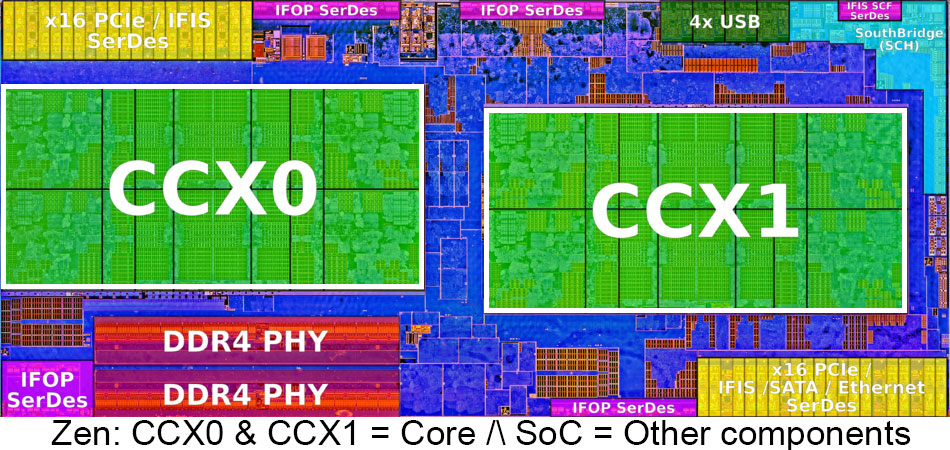
What is VDDCR SOC Load Line Calibration?
SOC LLC adds extra voltage to compensate for Vdroop when uncore is put under heavy load LLC gives overclocking stability by preventing low or high voltage fluctuations and tries to maintain a stable voltage supply to the uncore. Higher LLC tends to overshoot more in voltage supply, and a lower LLC tends to undershoot in the voltage supply to the SoC.
What is VDDCR SOC Current Capability?
It is a threshold for the VRM to shut down and monitors the current supply to the SoC, setting Current Capability higher will allow for more current supply to the SoC but will increase heat output. This works best if you have an overclock that shuts down the motherboard/PC because the current threshold is triggered.
What is VDDCR SOC Switching Frequency?
Switching frequency is the transient response of your VRM MOSFETs settings this higher in Mhz will allow for a better transient response at the expense of increased heat output and using a lower setting in Mhz will lower the heat output but lower the transient response. Better transient response in overclocking translates into a more stable voltage supply to the SoC.
What is VDDCR SOC Power Phase Control?
This affects your VRM Power Phases to the uncore and will be depending on the setting, achieve greater stability in overclocking. Setting Power Phase Control to extreme keeps the number of active SoC power phases at the maximum If you set Power Phase Control to optimized there will be a power-saving, but less stability, phases to the CPU will power down.
What is VDDCR SOC Voltage?
This setting affects the voltage supply to the SoC components. It should be increased when overclocking the CPU core frequency/ratio to aid with better stability of the SoC components as well as the core components. Increasing the VDDCR SOC Voltage will increase the heat output of the CPU package as a whole.
What is CPU Core Ratio?
Sets the clock rate of your CPU by a factor of 10X. So a Core Ratio of 40.00 will multiply the external clock with a base value of 100 to 4,0Ghz.
What is VDDCR CPU Voltage?
Sets the voltage for your CPU on a 1:1 ratio, depending on your motherboard you can either enter a manual value of an offset value. So a value of 1.4000 will set the CPU voltage to 1.4 volts using the manual setting.
What is FCLK?
Stands for Infinity Fabric Clock Speed(FCLK) and can be adjusted with the new Ryzen 3000 series(Zen2). In previous Zen and Zen+ architecture, the Infinity Fabric Clock speed would be set by the DRAM frequency(MCLK). Ideally, you want FCLK to run synchronously(1:1 ratio) with the MCLK for best performance. In short, a DDR4(Double Data Rate) kit is rated for 3600Mhz MCLK and therefore will run synchronously with 1800Mhz FCLK, a 1:1 ratio.
What is the GFX clock frequency?
Sets the clock rate of the internal Vega GPU on Ryzen APUs by a factor of 1:1, so a 1600 value translates into a 1600mhz GPU clock speed.
What is the GFX core voltage?
Sets the voltage for the internal Vega GPU on Ryzen APUs on a 1:1 ratio, so a manual value of 1.25000 is 1.25 volts.
What is AMD SAM?
Stands for Smart Access Memory and work with the AMD 5000 series CPUs and AMD 6000 GPU's. In short, it is a new way for your PC to access the whole memory capacity(VRAM) of an AMD 6000 series GPU. Previously this was done with 256MB paging of the VRAM called BAR(Base Adress Register). Depending on your motherboard brand it can be found in the PCIe section of the advanced menu or advanced settings and turn on Above 4G Encoding and Re-Size BAR Support.
What is DRAM Voltage?
Is the voltage supply to your RAM aka Memory sticks, increasing the DRAM voltage will allow your RAM to run at a higher frequency at times without changing the DRAM Timings but will increase heat output.
What is Global C-State Control?
This sets the idle states of a CPU when it is not executing commands there a various C-States and serve as a power-saving function. For overclocking, this should be turned off since you want maximum performance at the expense of increased power consumption and helps with keeping a stable overclock.
Closing thoughts.
The main reason to write this FAQ is to supplement guides for AMD Ryzen based CPU's found on this website, and I could not find a one-stop-shop solution for ensuring I nail the explanation for each BIOS settings correctly. You can find my guides for the AMD Ryzen CPU's in the bullet list below.
- Ryzen 5 overclocking the 1600.
- Ryzen 5 overclocking the 1600X.
- Ryzen 3/5 OC'íng the 2200G/2400G APU's.
- Ryzen 5 overclocking the 2600.
- Ryzen 7 overclocking the 3700X
- Enjoy overclocking, Paul "HisEvilness" Ripmeester








